Teaching pronunciation: a practical guide for language educators
 For language educators and learners, pronunciation is one of the most important skills to master. It plays a pivotal role in helping students communicate effectively and its impact goes way beyond just speaking correctly.
For language educators and learners, pronunciation is one of the most important skills to master. It plays a pivotal role in helping students communicate effectively and its impact goes way beyond just speaking correctly.
This blog post highlights and explores the best methods for teaching pronunciation, identifies why they work and provides practical examples that language teachers can use in their language classrooms to inspire and support students.
Getting L2 pronunciation right boosts speakers’ confidence and fluency, reduces miscommunication and prepares learners for real-life conversations. However, it can be challenging to teach and learners often don’t see desired results for a long time.
If you’d like to read more Sanako blog posts on teaching pronunciation, then do check out additional useful content here:
- How phonemic charts can help you teach English pronunciation
- Automatic pronunciation grading for developing students’ fluency and speaking skills
Why is pronunciation so important?
Before getting into the detail of how to teach it, let’s reiterate why pronunciation is such an important, yet often overlooked language learning skill in formal second language education. We believe there’s three main reasons to consider.
- Enhances comprehension: When learners articulate words correctly, it becomes easier for native speakers to understand them. Mispronounced words can lead to misunderstandings and hinder effective conversation. By improving pronunciation, learners can ensure that their messages are conveyed accurately and understood without difficulty.
- Boosts confidence: When learners can pronounce words and phrases accurately, they are more likely to speak up in class or engage in conversations outside the classroom. Confidence, after all, is a key factor in language acquisition and fluency.
- Real-life application: Language learners don’t just study a language for academic purposes; they aim to use it in real-life situations. In these contexts, clear pronunciation is crucial. Whether it’s ordering a meal at a restaurant, making a business presentation, or participating in a job interview, learners must articulate their thoughts and ideas clearly.
What are the best methods for teaching pronunciation?
Now, let’s explore the best methods for teaching pronunciation and how they can be applied in the language classroom. From our extensive experience of working with language educators worldwide, Sanako typically identifies the following key approaches.
1. Phonetics
This is the science of speech sounds and it’s a fundamental approach to teaching pronunciation. By building understanding of their L2’s sounds, teachers can help students to articulate words accurately.
To incorporate phonetics into your lessons:
- Introduce learners to phonetic symbols and the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA)
- Teach them to recognize and produce the distinct sounds of their target language
- Practice tongue placement, lip rounding and other articulatory features
Research has shown that incorporating phonetics into language teaching has several benefits. Derwing and Munro (2015), for example, found that phonetic training helps learners discriminate between subtle sound differences, making their pronunciation more accurate. Whereas studies by Golestani and Zatorre in 2009 indicated that phonetic awareness can improve word recognition skills, making learners more proficient in comprehending spoken language.
2. Mimicry - Learning by imitation
This simple yet effective method encourages students to mimic native speakers’ pronunciation patterns. Here’s how to use mimicry in your classroom:
- Play audio recordings of native speakers or use video clips
- Then ask students to repeat sentences, pay close attention to their intonation, stress and rhythm
- Encourage them to mimic the speaker’s tone and inflection
Again, there’s clear research evidence for the effectiveness of this approach. Celce-Murcia in 2001 argued that the most successful methodologies in L2 teaching and learning have included repetition and imitation of words and sentences to a greater or lesser extent. Whilst a 1988 study by Flege demonstrated that imitating native speakers could help learners acquire the natural intonation and rhythm of a language, leading to more fluent and comprehensible speech.
3. Minimal pairs - Spotting the difference
These are words that differ by only one sound, which makes them an excellent tool for practising specific pronunciations. To incorporate minimal pairs into your lessons:
- Provide a list of word pairs that only differ by a single sound (e.g., “ship” and “sheep”)
- Get students to listen carefully and identify the differences
- Practice pronouncing these word pairs to master the distinct sounds
Research published by Hansen in 1995 found that “language teachers can improve their students’ pronunciation markedly drilling minimal pairs in order to help them improve their intelligibility,” Whilst Rajadurai, 2001 notes that the approach makes “students more conscious of their own pronunciation and aware of ways in which their pronunciation differs from the model offered.”
Practical classroom ideas for teaching pronunciation
Now, let’s explore some actionable ideas that can be easily applied in your language classroom. Try to ensure that such lessons are always engaging, that the activities are fun and that students are kept motivated when actively producing language.
1. Tongue Twisters and Rhymes
These are excellent, easy-to-use tools for improving pronunciation. They constantly challenge students to practise articulating difficult sounds and rhythms and can be easily adapted to suit different language levels.
Here are a few common examples in different languages:
- Portuguese: “O rato roeu a roupa do rei de Roma.”
- Spanish: “Tres tristes tigres tragan trigo en un trigal.”
- French: “Les chaussettes de l’archiduchesse sont-elles sèches, archi-sèches ?”
- German: “Fischers Fritze fischt frische Fische. Frische Fische fischt Fischers Fritze.”
- English: “She sells seashells by the seashore.”
Competitions: Organise friendly pronunciation competitions where students take turns reciting challenging tongue twisters. Award small prizes or recognition to the most articulate speakers.
Homework assignments: Assign students different tongue twisters or rhymes to practise at home and to then recite in the next class. Encourage them to record themselves for self-assessment.
Theme-Based tongue twisters: Connect tongue twisters and rhymes to the current lesson theme. For example, if the class is learning about food, use tongue twisters related to food and dining.
2. Role-plays and dialogue
Such activities give students authentic conversation scenarios for pronunciation practice and highlight the importance of clear and correct communication.
Realistic scenarios: Create role-plays based on everyday situations such as ordering food, asking for directions or making a phone call. This helps students practise pronunciation in contexts they might actually encounter.
Dialogue practice: Give students short passages of dialogue and ask them to rehearse and deliver these scripts in pairs or small groups. Encourage their peers to listen out for proper pronunciation and stress patterns. This can be done face-to-face or online via tools such as Sanako Connect.
Record and reflect: Encourage students to record their role-plays or dialogues. They can then listen to the recordings and self-assess their performance. Alternatively, they can get useful feedback from classroom peers.
3. Educational technology tools
As the tech company Apple famously first said: “There’s an app for that!” Unsurprisingly there’s a wide range of online tools that help learners practise and improve their pronunciation. They also help make language studies more accessible, effective and engaging.
More commonly, online language learning platforms such as Sanako Connect now include pronunciation functionality with automatic grading as a core part of their product. These tools help students to master speaking and pronunciation in their L2 by listening and repeating native-like speech models. Sanako’s solution also provides automatic feedback and scoring to users, as well as operating in most international languages instead of focusing on the English language only.
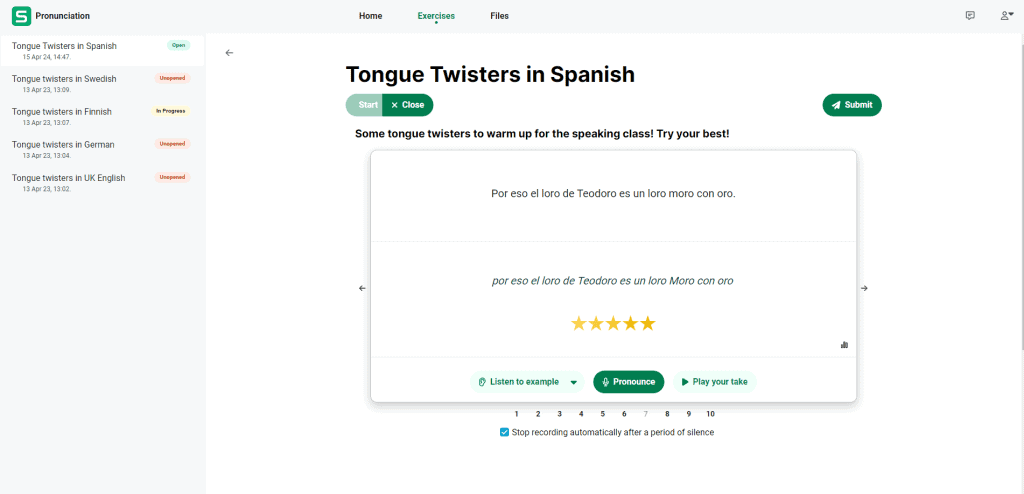 Educators could also share online resources with their students that provide pronunciation guides and audio examples for different accents.
Educators could also share online resources with their students that provide pronunciation guides and audio examples for different accents.
How can Sanako products support educators in teaching pronunciation skills?
Whatever lesson activity you decide to use, language teaching technology tools can play a vital role in building your students’ English or Foreign language pronunciation skills. In particular, Sanako’s language teaching tools help educators to:
- Boost your students’ confidence in speaking a foreign language with Sanako Connect’s Automated Pronunciation grading feature.
- Provide authentic speech models for students, who then record their own voice for comparison and receive immediate feedback.
- Create specific pronunciation tasks using a wide variety of media including sound files, text, presentations, videos and/or web pages.
- Invite students to assess tasks and supporting resources by simply clicking on a unique URL link. No login details are required, so there’s no data privacy or data storage issues for educators to worry about either!
- Create groups of students to conduct live group discussion and role-play activities. Teachers can listen in, give feedback in real-time and even record these individual group discussions for later review.
- Provide detailed and time-coded feedback: A piece of audio feedback can be carefully placed next to specific points of the student’s recorded oral submission where their pronunciation needs attention.
If you’d like to find out more about how Sanako’s dedicated language teaching solutions could transform your approach to teaching pronunciation skills, please contact us now to arrange your FREE demo!



